I. Overview?
Coprinus comatus, also known as hairy umbrella, hairy umbrella, thorn mushroom, belongs to the fungus Basidiomycotina subphylum Agaricus agaricus. Coprinus comatus is tender, delicious, and its color and flavor are no less than straw mushrooms. Coprinus comatus is also a medicinal mushroom, sweet and flat, beneficial to the spleen and stomach, soothe the nerves, cure phlegm and other effects, often eating helps to digest, increase appetite and acne treatment. According to the book “Chinese Medical Fungi Pictorial†and other books, the inhibitory rate of hot-water extract of Coprinus comatus on mouse sarcoma 180 and Ehrlich carcinoma was 100% and 90%, respectively. According to another report, Coprinus comatus contains an effective component for the treatment of diabetes, which is administered to mice in a weight of 2 grams of Coprinus comatus per kilogram of body weight. The effect of lowering the blood glucose concentration is most pronounced after 1.5 hours. In recent years, the United States, the Netherlands, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan have succeeded in cultivating Coprinus comatus, and their production of fresh mushrooms, dried mushrooms (cutting mushrooms), and canned mushrooms has become very popular in the international market. ?
In order to develop this valuable edible and medicinal mushroom resources, scientists and technicians from Fujian Sanming Fungal Research Institute, Shanxi Institute of Biology Research, Yunnan Edible Mushroom Science and Technology Development Center, Liaoyang Edible Fungi Research Institute and other units performed on Coprinus comatus. Investigations, collections, separations and cultivation experiments have done a lot of work for the commercial production of Coprinus comatus. Hebei Province and Beijing have been successfully planted, and there is currently a small supply market with considerable potential for production and markets. ?
Second, biological characteristics?
1. Morphological characteristics?
Sub-entities group. Mushroom bulbs have cylindrical caps, and they resemble turkey legs in the form of a stipe. Coprinus comatus is named after this. The late cap was bell-shaped, 9 to 15 centimeters high, and finally spread flat. The initial surface of the cap is smooth, and the epidermis dehisces. It becomes flat scales. It is white at the beginning, medium rust, and then deepens. The fungus is white and thin; the stipe is white, and it has a filigree luster. The fiber is 17 to 30. Centimeter, 1 to 2.5 centimeters thick, fine on the bottom, bacteria ring milky white, crisp, thin, easy to fall off; dense pleats, and stipe free, 5 to 10 mm wide, white, later turned black, soon appeared inky liquid. Spores are black, smooth, oval, and cystoid. The capsule is colorless, sticky, blunt at the top, slightly curved and sparse. ?
2. Ecological habits?
(1) Habits After spring, summer and autumn rain, they were born in fields, forest gardens, roadsides, and even on the roofs of huts. When the fruiting body matures, the pleats darken and the edges liquefy. Preservation period is very short, edible, but a small number of people have a slight poisoning reaction after eating, especially in the same food with wine or beer, it is easy to cause poisoning. ?
(2) Distribution is common in all countries. China is mainly produced in North China, Northeast China, Northwest China, and Southwest China. Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Gansu, Qinghai, Yunnan, and Tibet have all reported. The author also collected in the mountains of Haidian District, Beijing. ?
3. Living conditions?
Coprinus comatus is a kind of grass rot native bacteria with strong adaptability. The living conditions are as follows:
(1) Nutrition Coprinus comatus can use a wide range of carbon sources. Glucose, xylose, galactose, maltose, raffinose, mannitol, starch, cellulose, paraffin can all be used. The use of xylose is worse than glucose and the use of lactose is quite good, but it is not the best; some strains use galactose and lactose better than mannitol, glucose, fructose; the ability to use soft paraffin is poor. ?
Peptone and yeast powder are the best sources of nitrogen for Coprinus comatus. Coprinus comatus can use a variety of ammonium salts and nitrate nitrogen, but inorganic nitrogen and urea are not the most suitable nitrogen source. Adding asparagine, peptone, and urea in malt extract medium can promote better mycelial growth. The growth of Coprinus comatus is affected when thiamine is missing. Adding a natural matrix containing vitamin B?1 to the culture medium, such as malt extract, corn, oats, peas, lentils, red beets, wild peas, red clover, sorghum and other green leaves, can greatly promote coprinus comatus The growth of mycelium. ?
Coprinus comatus can be cultured in depth. In wort medium, 25 to 28 grams of dry mycelium can be produced per litre. In mycelia containing only sterile water, phosphate and carbon sources, mycelium of Coprinus comatus can also grow. ?
(2) Temperature The growth temperature of coprinus comatus mycelium ranges from 3 to 35°C, and the optimum growth temperature is 22 to 28°C. The cold-resistance ability of coprinus comatus hyphae is quite strong, and when the temperature is minus 30°C in winter, the coprinus mycelia in the soil can still survive safely. When the temperature is low, the mycelium grows slowly, showing fine, thin, villous; when the temperature is high, the mycelium grows quickly, the villous hyphae develop well, and the mycelium in the base becomes thin; when the mycelium is more than 35°C, autolysis occurs. phenomenon. The formation of fruiting bodies requires low temperature stimulation. When the temperature drops to 9 to 20°C, the buds of Coprinus comatus will come out one after another. Below 8°C or above 30°C, fruit bodies are not easily formed. In the range of 12 to 18°C, the temperature is low, the fruiting bodies are slow to develop, and the heads are large. Each is like a chicken leg, even like a grenades. Above 20°C, the stipe can easily extend and open. Artificial cultivation, the temperature at 16 ~ 24 °C when the largest number of fruiting bodies, the highest yield. The temperature is low, the fruiting body grows slowly, but the cap is large and thick, the stipe is short and strong, the quality is good, and the storage period is long; when the temperature is high, the growth is fast, the stipe is elongated, the cap is thin and the quality is reduced, Easily open and self-dissolve. ?
(3) Humidity The moisture content of Coprinus comatus culture materials is 60% to 70%, and the air relative humidity is about 80%. When the fruiting body occurs, the relative humidity of the air should be 85% to 95%, less than 60% of the surface of the surface of the cap of the mushroom, and when the humidity is more than 95%, the cap of the mushroom will be easily spotted. ?
(4) Light does not require light to grow in the mycelium of coprinus comatus, but 500 to 1 000 lux of light are required for the differentiation of mushroom buds and the development of fruit bodies. ?
(5) Fresh air is required for mycelium growth and fruit body growth of C. comatus. In the mushroom house cultivation, the ventilation period should be 4-8 times per hour during the formation of the fruit body. ?
(6) Acidity and alkalinity The coprinus comatus hyphae can grow in a medium with a pH of 2-10. The initial pH value of the medium is 3.7 or 8, and after the growth of the coprinus mycelia, the pH is automatically adjusted to about pH 7. Therefore, it is most suitable when the pH value is 6 to 7 regardless of the medium or the cover soil material. ?
(7) It should be particularly pointed out that the formation of the fruit body of Coprinus comatus requires stimulation of the soil and soil metabolites. ?
Third, the cultivation method?
Coprinus comatus cutting culture method and the white mushroom are generally the same, in addition to the bacteria used, and living conditions are different, you can refer to the cultivation method of white mushroom.
1. Cultivation materials?
(1) Main materials Horse manure, cow dung, wheat straw, rice straw, cottonseed husks and mixed wood chips. ?
(2) Accessories bran, rice bran, corn flour, compound fertilizer, gypsum powder, lime powder and vitamin B1. ?
2. How to cultivate?
Coprinus comatus can be grown indoors and outdoors. Clinker cultivation, raw material cultivation can be. It can be planted in bags, or planted in a box or on a bed frame, or it can be planted with vegetables or fruits. The grower can adopt the most favorable cultivation method according to local environmental conditions.
3. Cultivation season?
Coprinus comatus can be cultivated from spring to early summer and from autumn to spring. Indoors and greenhouses can also be cultivated in summer, but the climate is hot and difficult to keep fresh. Without proper processing and preservation measures, commercial significance is not significant. ?
4. Cultivation site?
Outdoor cultivation can be performed in orchards, vegetable fields, and leisure fields. Indoor cultivation can use the existing mushroom house, bed frame cultivation management. ?
Fourth, bacteria production?
1. Female production?
Coprinus comatus strains are mainly obtained by tissue separation method to obtain pure strains. The coprinus comatus hyphae grew well on PDA medium (200 g potatoes, 20 g glucose, 20 g agar, and water added to 1 000 ml). The mycelium grows better on the following rich medium or on the wheat frying medium. ?
(1) Potato 200 g, glucose 20 g, magnesium sulfate 1.5 g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5 g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1.5 g, vitamin B1 10 mg, agar 20 g, and water was added to 1 000 ml. ?
(2) 200 grams of wheat, soak for 10 hours, cook for 30 minutes, filter the juice, add 20 grams of glucose, 3 grams of peptone, 0.5 grams of magnesium sulfate, 1.0 grams of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2 grams of vitamin B-1, and 20 grams of agar. Add water to 1 000 ml. ?
(3) 250 grams of wheat, soak for 10 hours, cook for 30 minutes, filter the juice, add 150 grams of potato, 20 grams of glucose, 2 grams of peptone, 1.5 grams of magnesium sulfate, 1.5 grams of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.5 grams of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, Vitamin B1 10 mg, agar 20 g, add water to 1000 ml. The mycelium is initially white and then turns gray and the color of the medium is also deepened. In the incubator, hyphae can be covered with slant at 7 to 10 days at 25°C, the fastest 5 to 6 days. ?
2. Original production?
Using straw, cottonseed husks, and mixed wood chips as the main production medium and wheat production medium. Tests have shown that mycelia of Coprinus comatus can grow normally on these several media, but grow best on media dominated by wheat kernels and cotton seed hulls. The formulation of various original culture media is as follows:
(1) Straw culture medium straw (cut or crushed) 60%, bran 25%, corn powder 8%, compound fertilizer 5%, sugar 1%, lime 1%. ?
(2) Cottonseed husk medium A cottonseed hull 90%, bran 4.5%, corn flour 4.5%, lime 1%. ?
(3) Cottonseed husk medium B Cottonseed hull 87.5%, bran 10%, urea 0.5%, lime 2%. ?
(4) Cottonseed hull culture medium C cottonseed hull 78%, bran 10%, corn flour 5%, compound fertilizer 5%, sugar 1%, gypsum 1%, vitamin B1 trace. ?
(5) Sawdust medium: 75% of mixed wood chips, 15% of bran, 8% of corn flour, 1% of sugar, 1% of gypsum powder, and trace amount of vitamin B-1. ?
(6) The wheat culture medium is filled with water and soaked for 10-15 hours. Add 1% lime powder to boil for 30 minutes (no white heart, and the skin is not broken). Slightly dry and bottling. ?
The water content of the above culture medium is controlled at 60% to 65%, all the culture medium maintains the natural pH value, and the bottle is bottled according to the conventional method, and the tampon is plugged and sterilized by normal pressure or high pressure steam. After cooling, access to the parent species is performed aseptically in a sterile or sterile room and incubated in a 24-26[deg.] C. greenhouse or in an incubator. After 30 to 35 days of coprinus mycelium can fill the whole bottle. In addition to solid strains, the original species of Coprinus comatus can also be cultured in liquid medium to make a liquid stock. The elimination of agar in each parent culture medium formula can be used as a liquid medium formulation. ?
The quality of Coprinus comatus strains has a great impact on fruit body production and should be noted. Different strains, the morphology of mycelium is not exactly the same. Some strains were originally linear, and then gradually produced aerial hyphae; some strains were initially cotton-like, and later gradually became linear, with a white or gray color. Good strains have strong ability to use culture materials, and mycelia grow faster. ?
3. Cultivated species production?
(1) Culture medium?
1 with the above original medium formulation. ?
2 78% of miscellaneous wood, 20% of bran, 1% of calcium carbonate, 1% of sucrose, the ratio of material to water is 1:1.5, and the pH value is natural. ?
3 Mushroom compost 28%, sawdust 60%, bran 12%, feed water ratio 1:1.4 to 1.5, pH is natural. ?
(2) Production method The cultivar culture vessel was a polypropylene plastic film bag (length 34 to 36 cm, width 14 to 17 cm, thickness 0.05 to 0.06 cm). ?
1 specific operation. Select the above medium formulation, prepare the raw and auxiliary materials as required, add water and stir evenly, and then bag.
When bagging, first grab 2 to 3 pieces of culture material into the bag, press the corner of the bag into the bag by hand, and compact the culture material to make it into a cylindrical shape, and the bottom of the bag can stand upright on the ground. Insert a round wooden stick or a test tube with a diameter of 2 to 2.5 cm in the bag, preferably inserted in the end, but avoid piercing the bag, and then continue to press the hand while loading the material, and install it to the bag length of 2/3 (about 500 g of dry material), flatten the table and pull out the stick or test tube. In this way, the pre-embedded pipe (rod) is reloaded obliquely, and the cave left after being pulled out is firm and is not easy to be blocked during the transportation process. During sterilization, the steam easily penetrates the culture material, the sterilization can be more thorough, and the original species is dropped when inoculated. The bottom of the hole accelerates mycelial growth and shortens cultivation time of cultivars. After cultivating the material, clean the bag mouth and surface, and put a hard plastic collar (3.5 cm in inner diameter and 3.5 cm in height) on the mouth of the bag to allow the bag mouth membrane to pass through the ring and turn outwards toward the ring wall. Turn over, then flatten the bag, stuff the tampon and sterilize it. In order to prevent the tampon from getting wet, kraft paper must be placed on top of each plastic bag after the pan. Sterilize at 1.5 kg/cm2 steam pressure for 1.5 hours, or autoclave for 8 to 10 hours. Remove and cool after sterilization. ?
2 Inoculation and culture. Cultivated species should also be inoculated aseptically in the aseptic or sterile room and cultivated under the same conditions as the original species.
Fifth, cultivation process?
1. Clinker cultivation?
Cultivation rods were produced in the same manner as cultivars. After the bags of cultivated good bacteria are unpacked, they shall be discharged horizontally or vertically into the alfalfa. The gap between the bacterial rods shall be 2 to 3 centimeters, filled with manure, 30 sticks of bacteria should be discharged per square meter, and after the discharge is completed, about 3 centimeters of soil shall be applied. . If the soil is too dry, it can be sprayed with water and then covered with a polyethylene plastic film previously soaked in 5% sour. ?
Researchers from Jiangsu Province have conducted comparative tests on horizontal or vertical rows of fungus rods, indicating that the vertical discharge mushroom is faster and has higher biological efficiency. Cover soil should be divided into two steps, first fill in the soil between the bacteria bar, immersed in water and then cover the soil on the surface of the bacteria stick about 3 cm thick fine soil, watering with the spray to avoid soil compaction, and conducive to mushrooming. Cover soil with a thickness of 0.5 to 1 cm, not more than 2 cm. The relative humidity of the air in the cultivation room was kept at 85%-90%, and the temperature was adjusted to 16-22°C. Outdoor or greenhouses should have shade measures to avoid strong light. One week later, the hyphae resumed growth and joined into pieces. The plastic film was sprayed on the water every day and ventilation was added to stimulate the kinks of the mycelium to form mushroom buds. After the buds broke ground, ventilation and humidification were the main management factors. After more than 10 days of meticulous management, the sub-entities are rapidly growing up, about seven mature, that is, timely harvest. ?
2. Raw material cultivation?
The cultivation of Coprinus comatus with raw materials is more practical than cultivating Coprinus comatus. Practice has proved that both the north and the south can be promoted. ?
(1) Preparation of culture materials?
1 cottonseed husk or floor waste cotton 100 kg, quicklime 2 ~ 3 kg (some plus 0.1% of carbendazim or thiophanate-methyl), moisture content of 60% to 65%. ?
2 cottonseed husk 100 kg, phosphate fertilizer 2 kg, urea 0.5 kg, lime 2 kg, water 160 kg. ?
3 corn cob (crush) 100 kilograms, urea 1 kilogram, lime 2 kilograms, water 150 to 160 kilograms. ?
4 Straw (cut or crush) 40 kg, corn straw powder 40 kg, horse dung (dry manure and broken) 20 kg, urea 1 kg, phosphate fertilizer 2 kg, lime 3 kg, water 150 kg. ?
5 Flammulina velutipes ç³ 80 kg, 20 kg of equine feces, 1 kg of urea, 2 kg of phosphate fertilizer, 4 kg of lime, and 150 kg of water. ?
(2) Cultivation and Management
The culture medium is fully mixed and the accumulated material is 1 meter high and 1.2 to 1.5 meters wide, and the length is not limited. Cover with a plastic film and keep it warm. Turn it at 60-70°C for 10 hours and turn it over. When the temperature reaches 60-70°C, keep it for 10 hours and the fermentation is over. After spreading, it shall be spread on a well-prepared surface, and the thickness shall be 10-20 cm. The seed shall be sown in 3 layers, and the seed amount shall be 15% of the culture material. After the sowing is completed, smooth the material surface, slightly pressurize, and finally cover 5 centimeters of loam or first cover with plastic film to keep warm and moisturize. After the mycelium grows well, remove the plastic film covering the soil, cover with coarse soil (pre-wet with lime water in advance, soil thickness 0.8-1.2 cm), and then cover fine soil, spray moisture. ?
In the open-air cultivation, after covering the soil, the arched plastic sheds should be protected on the surface, and the sheds should be 30-40 cm high. ?
The outdoor cultivation in the south will be sown from September to the end of harvest in May of the following year. Attention should be paid to changes in temperature, rainfall, wind force, etc. North China is cultivated in plastic greenhouses for heat preservation and moisturizing. It can be produced all year round except during the summer heat. ?
The yield of Coprinus comatus differs greatly due to different strains, culture materials and cultivation conditions. The yield per square meter is 4.5 to 18 kilograms, and the biological efficiency is mostly 20% to 70%, and good can exceed 100%. ?
6. Harvesting?
The coleoptera fruiting body is mature rapidly, and must be loosened during the period of mushroom buds and harvested when anti-crimping scales appear on the bell-shaped cap. If the fungal ring is loosened or shed after harvesting, the fruiting body will oxidize browning during processing, and the fungal rot will even self-dissolve out of the dark brown spore fluid and completely lose its commercial value. ?
VII. Sales and processing?
In the small-scale cultivation of Coprinus comatus, fresh-selling is the main product. Coprinus comatus is easily broken and has a short shelf life and should be sold as soon as possible. To supply the market away from the cultivation field, the mushroom buds of Coprinus comatus may be cut into thin slices, and then dehydrated and dried with an electric hot air dryer. Sliced ​​mushrooms in plastic bags, each package of 100 to 150 grams. ?
In addition, salted coprinus comatus or coprinus comatus can also be processed. Processing methods can be modeled on white mushrooms and straw mushrooms.
Sanwei External Fixator is designed by Hangwei. It has a complete product line in different parts. The clamp and spherical needle holder gives high flexibility in surgery. The material is carbon fibre or stainless steel.
Certification: CE & ISO13485
Material: Aluminium
Advantages of Sanwei External Fixator:
I. Unnular design, firm and reliable
II. Easier operation & short time
III. Minimally invasive surgery, no influence to blood supply of bone
IV. Second surgery is unnecessary, remove directly in clinic
V. Dynamic design, better for bone healing
VI. Taper bone screws, taut and firm after insertion.
We can also provide OEM service for you.
Hangwei Orthopedics Medical is a professional manufacturer of Sanwei External Fixator, and look forward to the cooperation with you.
We strive to provide superior benefits to professionals and patients through the development of reliable products.
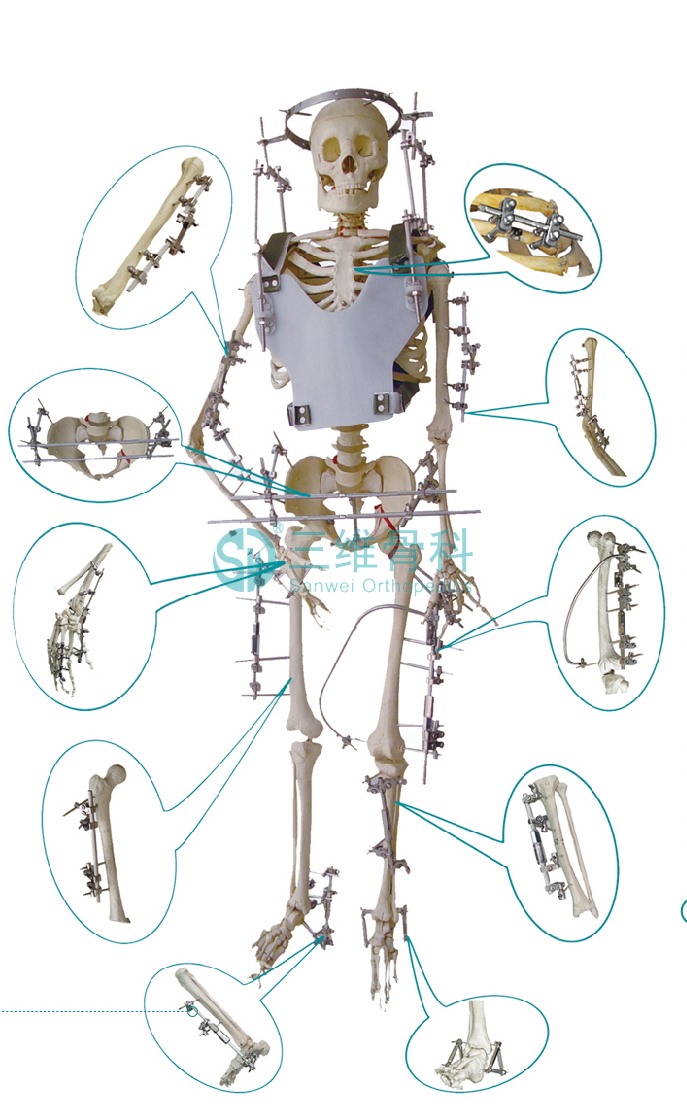
Sanwei External Fixator
Sanwei External Fixator,Sanwei External Fixator Femur,External Fixator Wrist,External Fixator Tibia
Shandong Hangwei Orthopedics Medcial Instrument Co., Ltd. , http://www.hangweimedical.com