Release date: 2017-03-27
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor of the digestive tract with clinical manifestations of occlusion, rapid development and poor prognosis. Pancreatic cancer has the lowest survival rate among all major cancers, and one of the most important reasons is the lack of diagnostic tools to detect the disease in its early treatable stage.
Recently, a research team led by Dr. Lev T. Perelman, director of the Center for Advanced Medical Imaging and Optics at BIDMC, developed a significant new tool that uses scattering spectroscopic techniques and diagnostic algorithms. Rapid differentiation of benign cysts of the pancreas, cancerous and precancerous cysts with an accuracy of up to 95%. The traditional preoperative detection accuracy is only 58%. The team's preliminary research results were published last week in the journal Nature, the journal Biomedical Engineering [1].

Pancreatic cancer is usually detected at an advanced stage and has a poor prognosis. According to the medical community, in the 21st century, pancreatic cancer has replaced liver cancer and become a new "cancer king." The reason why pancreatic cancer is called "cancer" is because it has a high incidence rate and is difficult to detect early. Once it is found that more than 50% is advanced, the mortality rate of pancreatic cancer is high, and the 5-year survival rate is less than 5%. Basically, how many people are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer each year, how many people die [2].
Professor Perelman said: "About one-fifth of pancreatic cancers occur in pancreatic cysts, but not all pancreatic cystic lesions are cancerous." Currently, doctors usually rely on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy. (EUS-FNA) to detect the tumorigenicity of pancreatic cysts. Tissue fluid is extracted from the cyst and then tested for the presence of cancer cells or indicative signs of disease.
However, because cyst fluids usually contain very few cells, fluid chemical analysis also lacks accuracy, and this assay is only 58% accurate. And this 58% accuracy often leads to more terrible consequences. Not only will the early detection and treatment of early pancreatic cancer be severely delayed, but inaccurate diagnosis will also expose patients to unnecessary pancreatic surgery. Knowing that moving a knife on the pancreas is a huge risk.
There is a saying that pancreatic cancer surgery is the most difficult in general surgery. General surgery is divided into four levels according to the difficulty coefficient. Pancreatic cancer surgery is the most difficult fourth stage, and the surgical procedures are many and complicated. The pancreas is the most secretive organ in the abdominal cavity, involving the most blood vessels and organs. The anatomical structure is the most complicated, and a slight accidental operation can cause massive bleeding. Surgery usually involves removal of the duodenum and a portion of the jejunum, while reestablishing connections between multiple organs. Such a big move, the incidence of postoperative complications of pancreas is much higher than other general surgery [3].

Pancreas and pancreatic cancer
When a patient has a cystic lesion of the pancreas, it is impossible to accurately diagnose whether it is a benign cyst or to choose a high-risk surgery. Even if it is diagnosed as pancreatic cancer, it is basically advanced. Faced with the high risk of pancreatic surgery and the extremely high mortality of advanced pancreatic cancer, it is clear that we need new diagnostic methods to accurately identify pancreatic cysts that require surgical intervention and do not require surgical intervention.
The new tool developed by the research team used the scattering spectroscopic technique (LSS) to analyze the structural changes in the cancerous or precancerous cells of the pancreas by analyzing the reflectance spectra of the tissues. A diagnostic algorithm was developed for this purpose to determine the cancerousness and benignity of the tissue based on the analysis of the spectrum. The results can be used to guide the doctor in determining whether the patient's pancreatic cyst requires surgery, thereby reducing the high risk of this decision.
In a series of experiments by Dr. Perelman and colleagues, LSS technology achieved 95% accuracy in the identification of pancreatic cysts. Although new technologies require further testing, LSS technology can definitely represent a significant advance in pancreatic cancer.
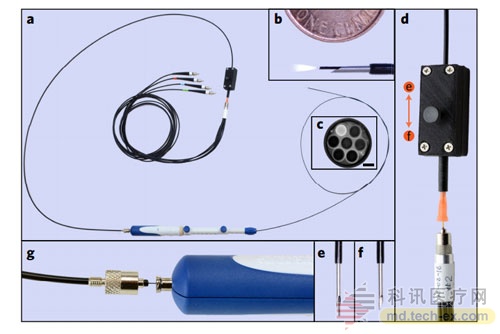
Fiber optic probe tool for use in body space
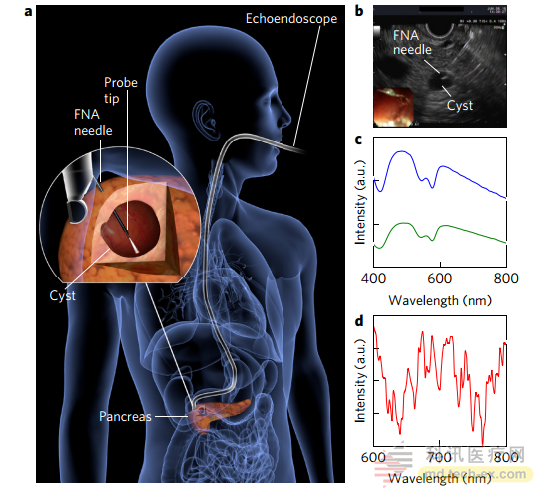
LSS detection and spectral diagnosis of cyst surface by fine needle aspiration in vivo under endoscopic ultrasound guidance
(Introduction through the mouth, the endoscope advances to the duodenum, and the FNA needle is used to penetrate the cyst under ultrasound guidance. The fiber extends from the tip of the probe to illuminate the position of the internal cyst surface.)
The researchers analyzed 13 reflectance spectra from recent intraoperative cysts and compared the results with other malignant tumor-determining methods, including preoperative imaging, FNA biopsy, and postoperative tissue analysis. According to the researchers, LSS technology has the same diagnosis in each case as postoperative analysis. In another test, the researchers inserted a miniature LSS fiber probe into the FNA probe. Nine patients who were diagnosed as cancerous or benign were diagnosed accurately by LSS technique [4].
The co-author of the article, Dr. Douglas K. Pleskow of the BIDMC Cancer Center, said that this is a revolutionary technique for the detection of pancreatic cysts. Using the new LSS technology and diagnostic algorithms to identify the malignant potential of pancreatic cystic lesions, with the advantages of high accuracy, fast, convenient and cheap. Not only does it provide great hope for timely differentiation of benign cysts of the pancreas, cancerous and precancerous cysts, but it also accurately identifies pancreatic cysts that require surgery.
If the new technology can be widely used, it can avoid unnecessary pancreaticoduodenectomy in many benign pancreatic lesions, and more importantly, it can identify malignant cysts that might have been missed, thus killing pancreatic cancer in the cradle. [4].
Reference materials:
[1] https://?winzoom=1
[2] http://cancer.39.net/a/121009/4064010.html
[3] http://health.sohu.com/20151020/n423718277.shtml
[4] http://
Source: Singularity Network
Window Screen
In generally, the Window Screen including stainless steel window screen, aluminum window screen, alloy window screen, fiberglass window screen, etc .
The weave type is flat weaving.
Surface treatment of window screen: painted, glavanized, PVC, etc .
The window screen is generally used in hotels, public construction, civil buiding block of the mosquitoes and other insects.
Advantages of window screen :
light weight
good toughness
embroidery
ventilated good corrosion resistance
easy to clean

Window Screen,Aluminum Window Screen,Plastic Window Screen,Stainless Steel Window Screen,Stainless Steel Wire Mesh
ANPING COUNTY SHANGCHEN WIREMESH PRODUCTS CO.,LTD , https://www.scwiremesh.com